- Clinical Study
- Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Detemir Administered Once Daily According to Two Titration Algorithms (3-0-3 and 2-4-6-8) in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Hea Min Yu, Kang Seo Park, Jun Hwa Hong, Keun Yong Park, Jong Min Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Yeo Joo Kim, Tae Kun Oh
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):142-148. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.142
-
-
4,723
View
-
80
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
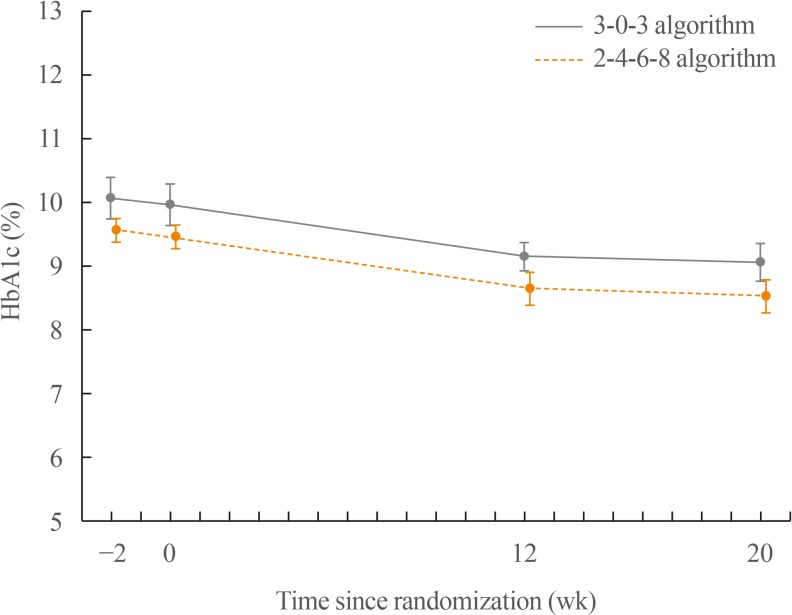
This study was conducted to compare glycaemic control with insulin detemir administered according to two titration algorithms (3-0-3 and 2-4-6-8) after 20 weeks of treatment in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin. MethodsThis was a 20-week, randomised, multicentre, open-labelled, treat-to-target trial. Forty-six patients were randomised in a 1:1 manner to either the 3-0-3 (G3, n=23) or 2-4-6-8 (G2, n=23) algorithm. The primary endpoint was change of haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and the secondary safety endpoint included hypoglycaemic events. ResultsAfter 20 weeks, HbA1c decreased similarly in the G3 and G2 groups, with a mean change of −0.9% from baseline. The mean change in fasting plasma glucose was numerically similar in both groups. The hypoglycaemia event rate per 100-patient-years of exposure (r) in the G2 group (r=1,427) was higher than that in the G3 group (r=807). ConclusionBoth treatment groups had numerically similar HbA1c reductions. A trend towards fewer hypoglycaemia episodes after dose stabilisation was seen with the simpler G3. Clinically, this may be an important observation, as a simpler titration algorithm may support self-management and maintenance of insulin therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Time for Using Machine Learning for Dose Guidance in Titration of People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review of Basal Insulin Dose Guidance
Camilla Heisel Nyholm Thomsen, Stine Hangaard, Thomas Kronborg, Peter Vestergaard, Ole Hejlesen, Morten Hasselstrøm Jensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; : 193229682211459. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of patient-led versus physician-led titration of basal insulin in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Marco Castellana, Filippo Procino, Rodolfo Sardone, Pierpaolo Trimboli, Gianluigi Giannelli
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001477. CrossRef
- Thyroid
- Natural Course of Cytologically Benign Thyroid Nodules: Observation of Ultrasonographic Changes
-
Dong Jun Lim, Jee Young Kim, Ki Hyun Baek, Mee Kyoung Kim, Woo Chan Park, Jong Min Lee, Moo Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(2):110-118. Published online June 18, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.2.110
-
-
4,264
View
-
36
Download
-
18
Web of Science
-
23
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
- Background
The natural course of cytologically benign thyroid nodules remains unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether ultrasonographic (US) changes are associated with changes in nodule volume during follow-up. MethodsWe retrospectively reviewed over 4 years of clinical records of patients with benign thyroid nodules as confirmed by fine needle aspiration (FNA). In total, 186 patients with 202 benign thyroid nodules were included for study. We assessed for changes in nodule volume and examined the cystic portion of the nodule as well as four US features (echogenicity, margin, calcification pattern, and shape). ResultsDuring follow-up (mean, 21.7±10.7 months) and using 50% as a cutoff value, nodule volumes increased in 11.8%, exhibited no change in 79.9%, and decreased in 8.3% of patients. Proportion of nodules demonstrating at least one US change was 20.8% (42/202). The most common US changes (in descending order of frequency) were cystic change, margin change, and calcification pattern change. Nodule shape and echogenicity rarely changed. Increased nodule volume was not significantly associated with any US features or with the number of FNAs but was associated with younger age at time of diagnosis. ConclusionAlthough a portion of thyroid nodules confirmed as benign showed US changes or volume changes during the follow-up period, these findings may only represent the natural course of benign nodules. Frequent follow-up with US might be needed for only a small number of cases with suspicious US findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Follow-up of benign thyroid nodules confirmed by ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy after inconclusive cytology on fine-needle aspiration biopsy
Yoon Ji Hwang, Hye Ryoung Koo, Jeong Seon Park
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(1): 121. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Approach and Outcome of Thyroid Incidental Findings vs. Clinically Overt Thyroid Nodules: An Observational Single-Centre Study
Tom Jansen, Nike Stikkelbroeck, Annenienke van de Ven, Ilse van Engen-van Grunsven, Marcel Janssen, Han Bonenkamp, Martin Gotthardt, Romana T. Netea-Maier
Cancers.2023; 15(8): 2350. CrossRef - Association between various thyroid gland diseases, TSH values and thyroid cancer: a case–control study
Leif Schiffmann, Karel Kostev, Matthias Kalder
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2020; 146(11): 2989. CrossRef - TI-RADS und andere sonografische Klassifikationssysteme für Schilddrüsenknoten
Julian M. M. Rogasch, Christoph Wetz, Winfried Brenner
Onkologie up2date.2020; 2(03): 223. CrossRef - TI-RADS und andere sonografische Klassifikationssysteme für Schilddrüsenknoten
Julian M.M. Rogasch, Christoph Wetz, Winfried Brenner
Radiopraxis.2020; 13(01): E1. CrossRef - Changes of Nodular Size and Its Risk Factors in Iodine-Sufficient Area: a Retrospective Cohort Analysis of 7753 Thyroid Nodules
Hwa Young Ahn, Kyung Won Kim, Hoon Sung Choi, Jae Hoon Moon, Ka Hee Yi, Min Kyung Hyun, Min Joo Kang, Jung Im Shim, Ja Youn Lee, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
International Journal of Thyroidology.2020; 13(2): 118. CrossRef - Comparison of Natural Course between Thyroid Cancer Nodules and Thyroid Benign Nodules
Kyun-Jin Yun, Jeonghoon Ha, Min-Hee Kim, Ye Young Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(2): 195. CrossRef - Risk factors for hypothyroidism in euthyroid thyroid nodule patients with lymphocytic thyroiditis on fine needle aspiration cytology
Jeong-Min Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Chan-Kwan Jung, So-Lyung Jung, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Dong-Jun Lim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(6): 1287. CrossRef - Evaluation of the natural course of thyroid nodules in patients with acromegaly
Sema Ciftci Dogansen, Artur Salmaslioglu, Gulsah Yenidunya Yalin, Seher Tanrikulu, Sema Yarman
Pituitary.2019; 22(1): 29. CrossRef - TI-RADS und andere sonografische Klassifikationssystemefür Schilddrüsenknoten
Julian M.M. Rogasch, Christoph Wetz, Winfried Brenner
Der Nuklearmediziner.2019; 42(03): 206. CrossRef - Molecular profiling of thyroid nodule fine-needle aspiration cytology
Markus Eszlinger, Lorraine Lau, Sana Ghaznavi, Christopher Symonds, Shamir P. Chandarana, Moosa Khalil, Ralf Paschke
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2017; 13(7): 415. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of thyroid nodule growth to predict malignancy in thyroid nodules with benign cytology: systematic review and meta‐analysis
Naykky Singh Ospina, Spyridoula Maraka, Ana Espinosa DeYcaza, Derek O'Keeffe, Juan P. Brito, Michael R. Gionfriddo, M. Regina Castro, John C. Morris, Patricia Erwin, Victor M. Montori
Clinical Endocrinology.2016; 85(1): 122. CrossRef - Rapid thyroid nodule growth is not a marker for well-differentiated thyroid cancer
Claudius Falch, Steffen Axt, Bettina Scuffi, Alfred Koenigsrainer, Andreas Kirschniak, Sven Muller
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Size of Benign Thyroid Nodules and Analysis of Associated Factors That Affect Nodule Size
Seok Ho Seo, Tae Hyun Kim, Soon Ho Kim, Seung Hyun Lee, Jong Taek Kim, Dae Won Park, Dong Chul Lee
Chonnam Medical Journal.2015; 51(2): 97. CrossRef - Thyroid ultrasound findings in a follow-up survey of children from three Japanese prefectures: Aomori, Yamanashi and Nagasaki
Naomi Hayashida, Misa Imaizumi, Hiroki Shimura, Fumihiko Furuya, Noriyuki Okubo, Yasushi Asari, Takeshi Nigawara, Sanae Midorikawa, Kazuhiko Kotani, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Akira Ohtsuru, Takashi Akamizu, Masafumi Kitaoka, Shinichi Suzuki, Nobuyuki Taniguchi, S
Scientific Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Natural Course of Cytologically Diagnosed Benign Thyroid Nodules
Eun-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2014; 7(2): 136. CrossRef - Ruling in or ruling out thyroid malignancy by molecular diagnostics of thyroid nodules
Markus Eszlinger, László Hegedüs, Ralf Paschke
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2014; 28(4): 545. CrossRef - Insufficient Experience in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Leads to Misdiagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Won Seo Park, Jong Kyu Byun, Yu-Jin Kim, Ja Min Byun, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 293. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Non-Diagnostic Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: Usefulness of the Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy
Sung Hak Lee, Min Hee Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Dong Jun Lim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2014; 21(6): 1870. CrossRef - Letter: Natural Course of Cytologically Benign Thyroid Nodules: Observation of Ultrasonographic Changes (Endocrinol Metab 2013;28:110-8, Dong Jun Lim et al.)
Sun Wook Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(3): 241. CrossRef - Natural Course of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Kyung Won Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(2): 94. CrossRef - Response: Natural Course of Cytologically Benign Thyroid Nodules: Observation of Ultrasonographic Changes (Endocrinol Metab 2013;28:110-8, Dong Jun Lim et al.)
Dong Jun Lim, Ki Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(3): 243. CrossRef
- A Case of Incidental Struma Ovarii Confounded with the Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Cancer.
-
Young Hee Jung, Sung Min Jung, Jong Min Lee, Yi Sun Jang, In Suk Lee, Jong Ok Kim, Hye Soo Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(3):227-231. Published online September 19, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.3.227
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A focal radioactive iodine uptake in the pelvis of a patient with differentiated thyroid cancer needs differential diagnosis besides bone metastasis. Struma ovarii is a rare monodermal ovarian teratoma composed predominantly of mature thyroid tissue; 5-10% of these tumors are malignant. As diagnosis and surgery of thyroid cancer have increased recently, incidental cases of struma ovarii, after radioactive iodine treatment, were occasionally reported. Rare cases of ovary metastasis of thyroid cancer were also reported. We report a case of benign struma ovarii incidentally found in a patient with papillary thyroid cancer. The patient showed a sustained high level of thyroglobulin and focal radioactive iodine uptake in the right pelvis, confused with distant metastasis, after total thyroidectomy and radioactive iodine treatment.
- A Case of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor with Recurrent Hypoglycemia.
-
Sun Hee Ko, Seok Hwan Kim, Il Ho Maeng, Koon Soon Kim, Yi Sun Jang, Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Suk Young Park, Sang Bum Kang
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(2):125-130. Published online June 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.2.125
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Non-islet cell tumor induced hypoglycemia (NICTH) is attributable to overproduction of insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) by solid tumors, and these tumors usually originate from mesenchymal or epithelial cells. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is a rare mesenchymal tumor and most commonly find in the gastrointestinal tract. It is usually expresses the CD117 (stem cell factor receptor, c-kit) detected by immunohistochemistry. Hypoglycemia associated with GIST is very rare and this has not yet been reported in Korea. A 72-year-old man was hospitalized due to frequent episodes of confusion. It was observed that non-hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, an elevated serum IGF-II level and a huge liver mass. The histology of liver mass showed c-kit (CD117) positivity, which was consistent with GIST, but it was surgically unresectable. He was treated with imatinib mesylate. Although he recieved palliative treatment, he still experienced intermittent fasting hypoglycemia. After 2 months, the serum IGF-II level was even higher than before. We changed imatinib mesylate to sunitinib malate and performed radiotherapy on the liver mass. Although the change of the liver mass was not significant, he did not suffer from hypoglycemia for three months afterwards.
- A Case of Early Gastric Cancer Coincidentally Developed in a Patient with Acromegaly.
-
Kyun Woo Park, So Young Lee, Hye Suk Son, Yi Sun Jang, Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):165-169. Published online April 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.165
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Acromegaly is associated with an increased risk for a variety of cancers such as colon cancer, prostate cancer and breast cancer. However, there have been few reports of gastric cancer developing in an acromegaly patient. A 66-year-old man suffered with diabetes mellitus and hypertension for 15 years, and he visited the endocrinology department due to dizziness. On physical examination, the biochemical studies and the sella MRI, he showed the typical features of acromegaly with pituitary microadenoma. During the cancer screening studies to find the cause of anemia, early gastric cancer was diagnosed by pathologic examination of the tissue biopsies. We described the summary of characteristics of the patient and reviewed literature.
- A Case of Atypical McCune-Albright Syndrome Associated with Hyperthyroidism.
-
Yi Sun Jang, Seok Hui Kang, Woong Ryoung Jung, Woo Tae Kim, Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Sung Dae Moon, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.158
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS) is a sporadic disease that's characterized by polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cafe-au-lait pigmentation of the skin, and multiple endocrinopathies, including sexual precocity, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, and hypercortisolism. Recent evidence has shown that the clinical manifestations are caused by a postzygotic activating missense mutation in the gene coding for the alpha-subunit of Gs protein that stimulates c-AMP formation in the affected tissues. Substitution of the Arg(201) residue in Gsalpha with cysteine or histidine have been identified in many MAS patients and Arg(201) to Gly or Leu mutations have also been recently identified. We identified the Arg(201) to His mutation in the gene encoding Gsalpha in the thyroid tissue from a 36-year-old man who was suffering with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia and hyperthyroidism.
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction in Young Woman with Graves' Disease and Atrial Fibrillation.
-
Young Yong An, Yi Sun Jang, Hyung Doo Kim, Ji Young Park, Hong Gun Bin, Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Suk Young Kim, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(5):528-534. Published online October 1, 2004
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Thyrotoxicosis associated atrial fibrillation occurs in 9 to 22% of hyperthyroidism patients; its prevalence increases after the age 60 years. Atrial fibrillation is known to be major independent risk factor for a thromboembolic stroke. The characterization of patient subgroups with atrial fibrillation, with high or low rate risk factor of a stroke, would help clinicians decide the benefit or harm to patient of long term anticoagulation therapy. Thyrotoxicosis, old age, hypertension, diabetes, heart failure, history of stroke and thromboembolism are all high risk factors for a stroke in atrial fibrillation patients. Thus, anticoagulation therapy is recommended for stroke prevention in those groups with atrial fibrillation and thyrotoxicosis. Herein is reported a case of acute cerebral infarction, with thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure, in a young woman
- Primary Hyperaldosteronism with Increased Plasma Renin Activity due to Secondary Hypertensive Renal Impairment.
-
Kang Woo Lee, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Dong Il Shin, Chee Ho Noh, Jung Min Lee, Jong Min Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(4):433-438. Published online August 1, 2003
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- An increased plasma aldosterone concentration, with suppressed plasma renin activity (PRA), is an abnormal finding in primary hyperaldosteronism. A suppressed PRA is caused by aldosterone- dependent sodium retention and extracellular volume expansion. A case of primary hyperaldosteronism, due to adenoma, with increased PRA, was observed. An adrenalectomy and intraoperative renal biopsy was performed. In our patient, histologically proven renal arteriosclerosis was the probable cause of the escape of the PRA from the suppression by an aldosterone-producing adenoma. Normal blood pressure was not attained after the adrenalectomy. However, the blood pressure was then controlled by small doses of antihypertensive drug before resection of the tumor. In this case, the patient was treated with spironolactone, but the blood pressure was not correctly controlled. After the adrenalectomy, the blood pressure was well controlled with smaller dose of calcium channel blockers. So, an early adrenalectomy may be beneficial as soon as the diagnosis of an aldosterone-producing adenoma is confirmed, even in patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis.
- A Case of Acute Rhabdomyolysis as a first Manifestation of Primary Hypothyroidism.
-
Jung Min Lee, Hyun Shik Son, Hye Jung Lee, Sook Hee Hong, Jong Min Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(1):79-84. Published online February 1, 2003
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Various symptoms, such as bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, constipation, myalgia, muscle weakness, delayed tendon reflex, and so forth, presented in hypothyroidism. Of these symptoms, muscle weakness, myalgia, and delayed tendon reflex are common features of hypothyroid myopathy. Acute rhabdomyolysis, a very severe form of myopathy, but is a rare manifestation of primary hypothyrodism. A 29-year-old man developed acute rhabdomyolysis, associated with primary hypothyroidism as a first manifestation. After thyroxine replacement therapy, he exhibited some improvement in muscle weakness and in non-pitting edema. We report a case of primary hypothyroidism presenting with spontaneous rhabdomyolysis as a first manifestation.
- Effect of Dexamethasone and 1,25(OH)2D3 on Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Cultured Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells.
-
Hye Soo Kim, Il Woo Lee, Jong Min Lee, Chang Hwan Han, Jin Hyung Sung, Min Young Park, Gil Son Khang, Hai Bang Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(2):206-217. Published online April 1, 2002
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
It is crucial, in the case of regenerating bone by tissue-engineering technique, that osteoblast progenitors are proliferated and induced to differentiate to osteoblasts sequentially at the proper time. Osteoblasts can be obtained from bone itself or from osteoblast progenitors in bone marrow, even though the amount of human marrow stromal cells in marrow aspirate is usually scanty. These cells, however, have been known demonstrate the potential to easily proliferate and differentiate in osteoblasts, chondroblasts or adipocytes according to different microenvironmental factors. We evaluated the effect of dexamethasone and 1,25(OH)2D3 on the proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of human marrow stromal cells in vitro. METHODS: We used twelve bone marrow aspirates obtained from different healthy bone marrow donors. Culture plates were randomly divided into the following four experimental groups; group 1 was cultured with control medium only, group 2 with control medium containing 1,25(OH)2D3, group 3 with control medium containing dexamethasone, and group 4 with control medium containing both 1,25(OH)2D3 and dexamethasone. 3H-thymidine uptake, protein content of cell lysates, alkaline phosphatase activities and alkaline phosphatase histochemistries were measured. Alizarin Red-S staining and quantification of dissolved dye were also performed. RESULTS: Combined stimulation of marrow stromal cells with both 1,25(OH)2D3 and dexamethasone was found to be effective to maintain stable long-term culture of the cells and to increased differentiation and mineralization of the cells. Synthesis and mineralization of matrix were highest when the cells were stimulated with 1,25(OH)2D3 alone during the early culture phase. However, 1,25(OH)2D3 shortened the lifespan of the cells. Interestingly, mineralization was higher in female donor cells than in male donor cells when stimulated with dexamethasone alone or with both dexamethasone and 1,25(OH)2D3. Neither 1,25(OH)2D3 nor dexamethasone affected cell proliferation. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that the synergistic effect of dexamethasone and 1,25(OH)2D3 is important in maintaining long-term culture and differentiation of human marrow stromal cells. It is preferable to administer 1,25(OH)2D3 after the attachment of cultured osteoblasts to biomaterials has been established, since it could shorten cell survival despite the great increase of mineralization at the early culture phase.
- Effect of Intermittent Etidronate Therapy on the Prevention of Bone Loss after Kidney Transplantation.
-
Hye Soo Kim, Jong Min Lee, Sung Kwon Kim, Cheol Whee Park, Chul Woo Yang, Moo Il Kang, Suk Young Kim, Sung Koo Kang, Byung Kee Bang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2001;16(4-5):426-437. Published online October 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Osteopenia or osteoporosis is one of the most frequently encountered complications in patients receiving various immunosuppressants after kidney transplantation. The few available preventive strategies for these complications tend to result in various outcomes. In this study, we evaluated the effect of intermittent etidronate therapy for the prevention of bone loss after kidney transplantation. METHODS: Fifty patients who received kidney transplantation for various reasons were recruited and followed for one year. Thirty-eight of these patients commenced etidronate treatment 7 days after operation, the other 12 were followed without etidronate therapy. The treatment consisted of 400mg of etidronate administered orally for 14 days, then repeated four-times every three months. Blood chemistry, iPTH and aluminium levels were tested periodically in all patients. Also checked were bone mineral density of the lumbar spine(L2-4) and femur at baseline, 6 and 12 months after kidney transplantation, as well as D-L spine lateral x-ray at baseline and 12 months. Serum osteocalcin and urine deoxypyridinoline were measured at baseline, 7 days and then every 3 months. RESULTS: Both the etidronate-treated and control groups showed significant decreases in bone mineral densities of the lumbar spine, femur neck and total femur at 6 and 12 months after kidney transplantation(p<0.005). Bone loss was significantly lower in the etidronate-treated group than the control at 12 months after kidney transplantation; lumbar spine(-3.54% vs. -9.51%, p<0.0005), femur neck (-5.41% vs. -8.91%, p<0.0005), total femur (-7.59% vs. -9.07%, p<0.005). Osteocalcin was decreased and deoxypyridinoline increased in both groups. No significant differences in the level or pattern of osteocalcin and deoxypyridinoline were observed in either group. New radiologic compression fractures were found in two patients of the treated group who exhibited severe osteoporosis at baseline during follow-up. CONCLUSIONS: The intermittent administration of etidronate seems to be effective in preventing rapid bone loss after kidney transplantation. Furthermore, this method is safe and convenient for administration and follow-up. Further studies will be required to elucidate the most effective treatment course for the prevention of fractures after kidney transplantation, especially in patients with established severe osteoporosis.
- A Case of Intrathyroidal Parathyroid Adenoma Diagnosed by Fine-Needle Aspiration.
-
Hye Soo Kim, Eun Kyung Lee, Sung Ha Hwang, Myung Sook Kim, Eun Hee Lee, Jong Min Lee, Suk Young Kim, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2000;15(4-5):614-621. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Fine-needle aspiration can be successfully utilized in the preoperative localization of abnormal parathyroid tissue. Fine-needle aspirate immunostaining for parathyroid hormone (PTH) or chromogranin and thyroglobulin (Tg) with measurement of PTH and Tg levels in the needle washings (FNAB-PTH and FNAB-Tg) can differentiate an enlarged parathyroid tissue from other cervical masses, such as thyroid nodules and lymph nodes. Parathyroid mass can be successfully aspirated by guidance of ultrasonography or computed tomography. Thyroid nodules are the most frequent cause of reduced accuracy of the imaging studies, such as ultrasonography, computer-assisted tomography and scintigraphy. We report on a case of unsuspected intrathyroidal parathyroid adenoma coexisted with thyroid follicular adenoma presenting two thyroid nodules. After biochemical diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism, we could not localize the parathyroid lesion specifically with any imaging method. Through fine-needle aspiration of two thyroid nodules, we performed the immunostaining for chromogranin and thyroglobulin and the measurement of PTH and thyroglobulin levels in the aspirated materials. The results confirmed the right nodule to be thyroid lesion and the left nodule to be parathyroid lesion preoperatively.
- A Case of Atypical Retroperitonealk Paraganglioma: Fatal paroxysmal adrenergic crisis and geart failure after sonographically guided biopsy of unsuspected paraganglioma.
-
Sung Koo Kang, Jong Min Lee, Sung Ro Yoon, Seok Young Kim, Jin Sung Moon, Hye Soo Kim, Young Jae Lee, Hye Kyung Bae, Hye Kyung Lee, Hyun Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(2):280-287. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Paraganglioma is an extraadrenal pheochromocytoma originating from chromaffin ceIls distributed in sympathetic nervous systems. This tumor often can produce catecholamines and induce sustained or paroxysmal hypertension, with or without the typical symptams of headache, palpitation and sweating. Paraganglioma without the usual clinical manifestations is not easy to suspect and diagnose. Herein, we report a case of atypical retroperitoneal paraganglioma which was thought to be the pancreas tail mass and result in a paroxysmal adrenergic crisis and fatal dilated cardiomyopathy after the sonographically guided percutaneous biopsy. This rare case warns against the usual practice of percutaneous biopsy for the preoperative diagnosis of intraabdominal or retmperitoneal tumors.
- A Case of Type II Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome: Acute adrenal crisis presented as the first manifestation of Addison's disease in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis and hypgonadism.
-
Young Sook Lee, Jong Min Lee, Hyun Ok Park, Sung Kyu Park, Sung Ro Yoon, Seok Young Kim, Bong Yeon Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(1):115-120. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Type II autoimmune polyglandular syndrome typically presents in adulthood. Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction are the most frequent manifestations. Addison's disease is the third major endocrine component of this disorder. In this report, we described a thirty-two year-old male patient who had hypogonadism, insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, and mild Addison's disease presenting its first manifestation as an acute adrenal crisis due to diabetic ketoacidosis. The ACTH concentration will be elevated early in the course of Addisons disease even before a significant reduction in the basal cortisol level or its response to exogenous ACTH occurs. Therefore, plasma ACTH measurements serve as a valuable screening study for Addisons disease.
- A Case of Cushing's syndrome due to Primary Pimary Pigmented Nodular Adrenal Dysplasia ( PPNAD ): A Case of Carney's Complex.
-
Soon Jib Yoo, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang, Youn Sik Kim, Jong Min Lee, Jong Man Won
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(1):90-98. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Primary Pigmented Nodular Adrenal Dysplasia (PPNAD) is a rare cause of Cushing's syndrome in infants and young adults. The familial occurrence, it may be variably associated with a complex of other pathologic characteristics that manifests extraadrenal disorders (includes cardiac myxomas, lentigines, mammary myxoid lesions, testicular tumors, pituitary adenomas, and neuroectodermal tumors) was considered indicative of Carneys complex. This was based on the failure of cortisol suppression by high-dose dexamethasone, either normal or suppressed basal adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels, and normal radiographic studies of the sellar turcica, and adrenals glands is almost normal or slightlg eulaged.. Bilateral adrenalectomy has thus the only effective means of cure. The disease may be a component of a rare, but potentially dangerous complex of abnormalities that follow an autosomal-dominant mode of inheritance. Recently we experienced a case of Carney's complex composed by Cushings syndrome due to PPNAD with familial purple colored lentigines on their lips and report it with reviews of the literatures.
- An Acromegalci Patient with Marked Tumor Shrinkoge after Continuous Infusion of Octreotide.
-
Je Ho Han, Hyun Sik Son, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Ku Kang, Yoo Bae Ahn, Sang A Jang, Ki Ho Song, Soon Jip Yoo, Jong Min Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):161-164. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
- Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mRNA by In Situ Hybridization in Normal and Abnormal Thyroid Tissue.
-
Hyun Sik Son, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Jong Min Lee, Kwang Woo Lee, Moo Il Kang, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang, Se Jeong Oh, Jin Han Kang, An Hee Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):337-343. Published online November 6, 2019
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Growth factors are polypeptide molecules that regulate cell growth and function by binding with high affinity to specific receptor molecules in the plasma membrane and stimulating receptor mediated action of intracellular signal transduction pathway.Epidermal growth factor(EGF) and their receptors(EGFR) regulate normal cellular growth, proliferation, and differentiation of various cells in vivo and in tissue cultures. And also may contribute directly to oncogenesis.Overexpression of EGFR and autocrine stimulation of growth involving this receptor system has been identified in several types of human neoplasia. There is evidence that the EGF and receptor system is involved in the regulation of follicular cell growth in the thyroid gland especially with immunohistochemical technic. But there was a challenge about the validity of previously performed immunohistochemical studies.In the study we investigated the relationship between EGFR mRNA expression and tumorigenesis by rapid in situ hybridization method. Formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded tissue sections of 10 normal, 17 nodular hyperplasia, 6 follicular adenoma, and 15 papillary cancer were examined. The results were as follows:1) EGFR mRNA positivity were 20%(2/10) in normal thyroid, 70%(12/17) in nodular hyperplasia, and 100% in follicular adenoma and papillary cancer.2) There was a significantly increased EGFR mRNA expression in papillary cancer compare to normal and nodular hyperplasia(p<0.05). But no difference was found with papillary cancer and follicular adenoma.3) There was a significantly increased EGFR mRNA expression in follicular adenoma compare to normal (p<0.05). But no difference was found with follicular adenoma and nodular hyperplasia. These results suggest that an overexpression of EGFR mRNA may play an important role in the tumorigenesis of thyroid tissue.
- Analysis of HLA-DQA1 genotype in Korea autoimmune thyroid disease and IDDM patients.
-
Moo Il Kang, Je Ho Han, Soon Jip Yoo, Jong Min Lee, Hyun Sik Son, Kun He Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Ku Kang, Choon Choo Kim, Dong Jip Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1992;7(4):320-330. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
|